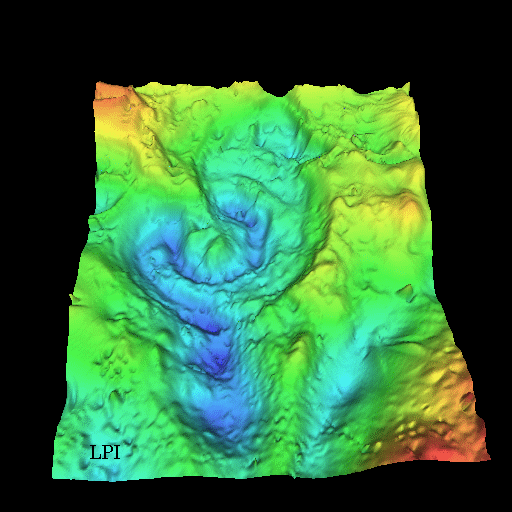
Impact! 65 Million Years Ago
Credit:
courtesy V.L. Sharpton,
LPI
What killed the dinosaurs?
Their sudden disappearance 65 million years ago,
along with about 70 percent of all species then living on Earth, is
known as
the K-T event (Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction event).
Geologists and paleontologists often
entertain the idea of a large
asteroid or comet impacting the Earth as the culprit.
Besides the firestorms, tidal waves, earthquakes, and hurricane winds
such an impact would generate, the
debris thrown into the atmosphere would have a serious global environmental
impact -- creating extended periods of darkness,
low temperatures, and acid rains.
In 1990, dramatic support for this theory came
from cosmochemist Alan Hildebrand's
revelation of a 65 million year old, 112 mile wide ring structure
still detectable under layers of sediment in the Yucatan Peninsula
region of Mexico.
The outlines of the structure, called
the Chicxulub crater
(named for a local village), are visible in
the above representation of gravity and magnetic field
data from the region.
In addition to having the right age, the crater is consistent with
the impact of an asteroid of sufficient
size (6 to 12 miles wide) to cause the global disruptions.
Regardless of the true cause of the K-T event, it is
fortunate that such impacts are presently believed to happen
only about once every 100 million years!