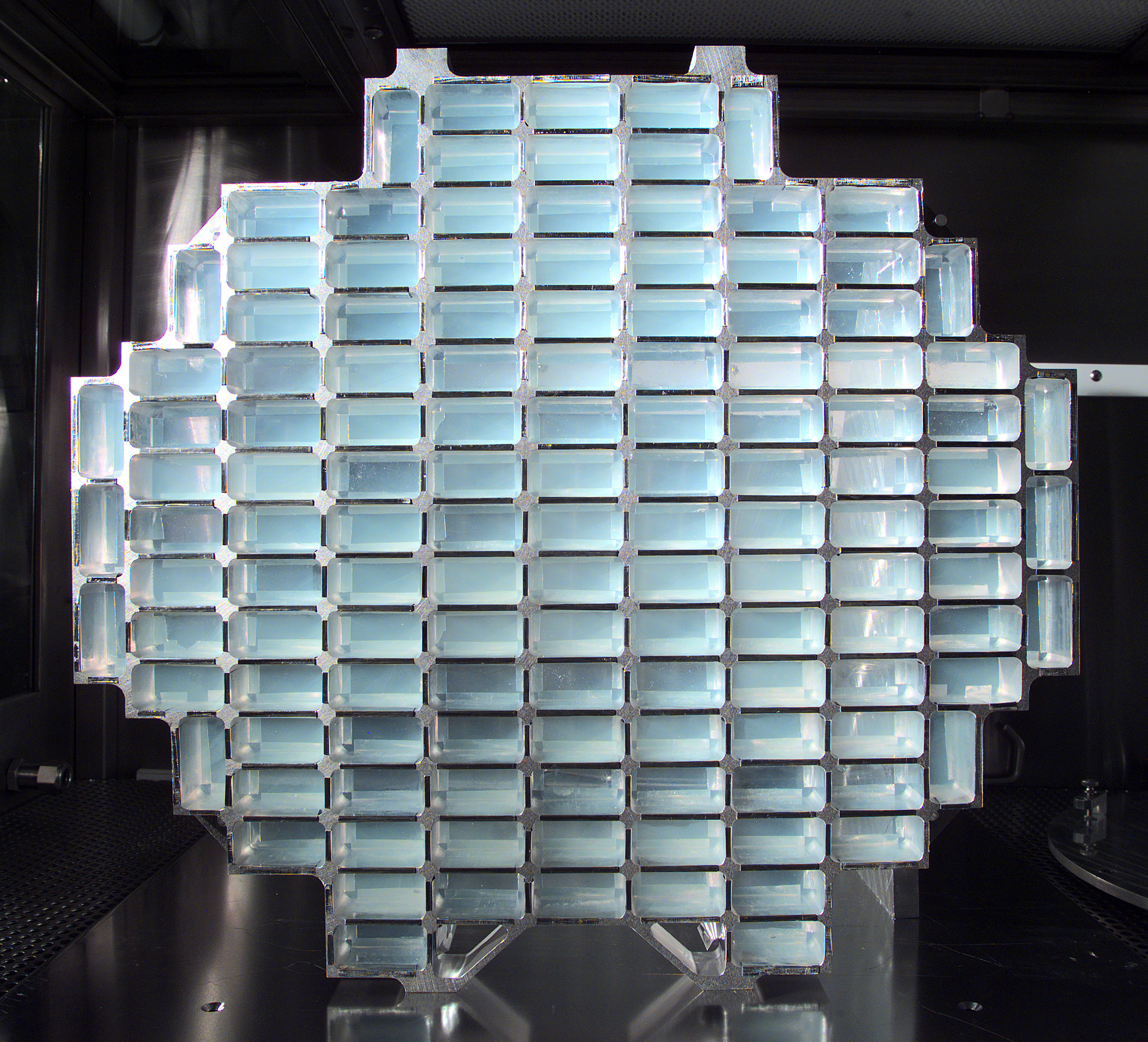
Aerogel For STARDUST
On February 7th,
this honey comb of aluminum cells filled with
aerogel was launched
on the STARDUST mission to interplanetary space.
STARDUST's goal is to capture dust from a
comet's tail and return to planet Earth -
the first sample return mission to
a comet!
This structure represents about 1,000 square centimeters of area
for collecting dust trailing within 150 kilometers of the nucleus of
P/Wild-2.
Comet P/Wild-2 is new to the inner Solar System.
Having spent its life in orbit between Jupiter and
Uranus, this comet was deflected in 1974 by a close
encounter with Jupiter
and now orbits between Jupiter and Earth.
Dust from P/Wild-2 should impact the aerogel at high speeds
and come to rest leaving
carrot-shaped tracks in
this amazingly tough, transparent,
ultra-low density material.
Returning to Earth by parachute in 2006,
the cometary dust sample will be analyzed
for clues to the formation and primordial composition
of our Solar System.