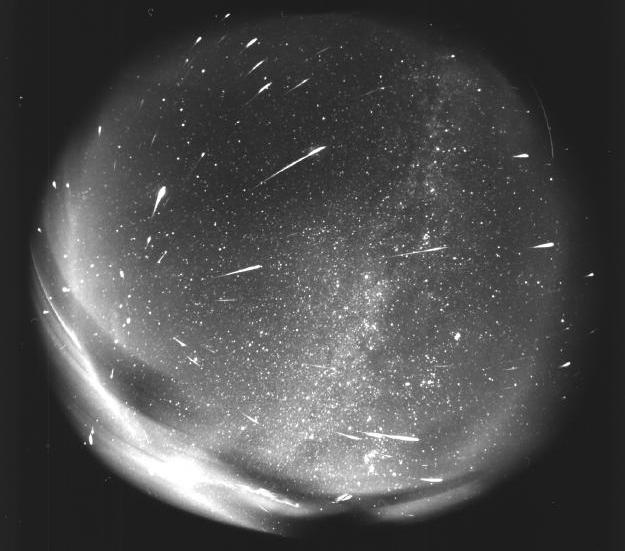
Leonids from Leo
Credit:
Juraj Toth
(Comenius U. Bratislava),
Modra Observatory
Is Leo leaking? Leo, the famous sky constellation visible on the left of the
above all-sky photograph,
appears to be the source of all the
meteors seen in this year's
Leonids Meteor Shower.
That
Leonids point back to
Leo is not a surprise - it is the reason this November
meteor shower
is called the Leonids.
Sand-sized debris expelled from
Comet Tempel-Tuttle
follows a well-defined orbit about our Sun,
and the part of the orbit that approaches
Earth
is superposed in front of the constellation Leo.
Therefore, when Earth crosses this orbit, the
radiant point of falling debris appears in Leo.
Over 150
meteors
can be seen in the
above four-hour exposure.
The
Geminid Meteor Shower, which appears to eminate from
the constellation of
Gemini, peaks this coming weekend.