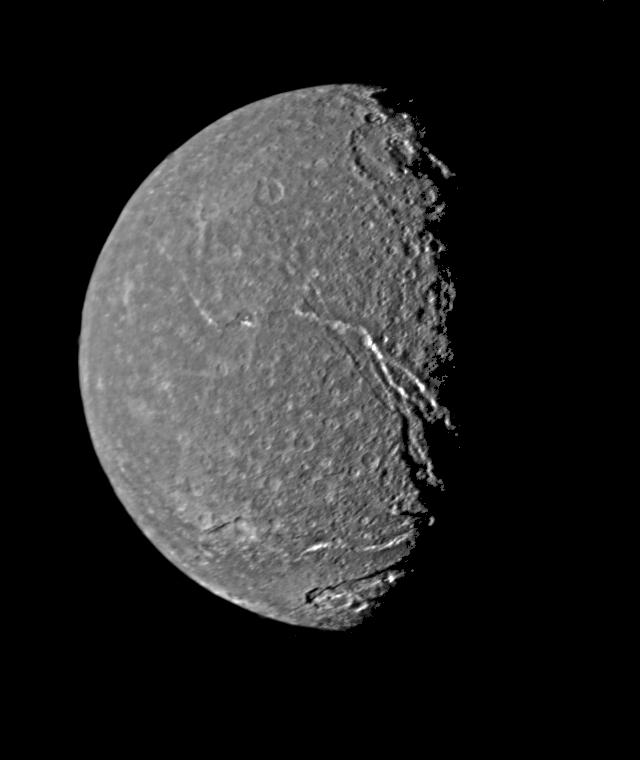
Titania's Trenches
Credit:
The Voyager Project,
NASA
British astronomer
Sir William Herschel discovered Titania and Oberon in
January of 1787.
He wasn't
reading Shakespeare's A Midsummer Night's Dream though,
he was making the first telescopic observations of moons of
the planet Uranus (a planet which he himself
discovered in 1781).
In January of 1986, nearly 200 years later,
NASA's robot explorer Voyager 2 became the only spacecraft to visit
the remote Uranian
system.
Above is Voyager's highest resolution
picture of Titania, Uranus' largest
moon.
The picture is a composite of two images recorded from a distance
of 229,000 miles.
The icy, rocky world is seen to be covered with impact craters.
A prominent system of fault valleys, some nearly 1,000 miles long,
is visible as trench-like features
near the terminator (shadow line).
Deposits of highly reflective material which may represent frost
can be seen along the sun-facing valley walls.
The large impact crater near the top,
known as Gertrude, is about
180 miles across.
At the bottom the 60 mile wide fault valley,
Belmont Chasma, cuts into crater Ursula.
Titania itself is 1,000 miles in diameter.