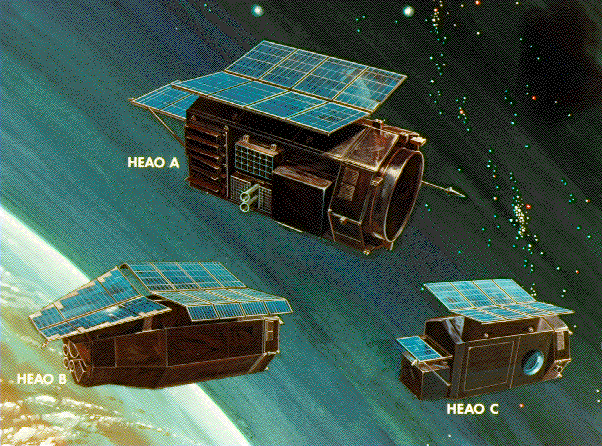A High Energy Fleet
Courtesy:
MSFC Historical Archive,
NASA
Looking like a fleet of futuristic starcruisers,
NASA's highly successful series of
High Energy Astrophysical Observatory (HEAO) spacecraft
appear poised over planet Earth.
Labeled A, B, and C in this vintage illustration,
the spacebased telescopes were known as
HEAO-1,
HEAO-2, and
HEAO-3 respectively.
HEAO-1 and HEAO-2 were responsible for revealing to earthlings
the wonders of
the x-ray sky, discovering 1,000s of celestial
sources of high-energy radiation.
HEAO-2, also known
as the Einstein
Observatory, was launched near the
date of the famous physicist's 100th birthday (November, 1978)
and was the first large,
fully imaging x-ray telescope in space.
HEAO-3, the last in the series,
was launched in 1979 and measured high energy
cosmic-ray particles
and gamma-rays.
These satellite observatories were roughly 18 feet long and weighed
about 7,000 pounds. Their missions completed, all have fallen from orbit
and burned up harmessly in the atmosphere.