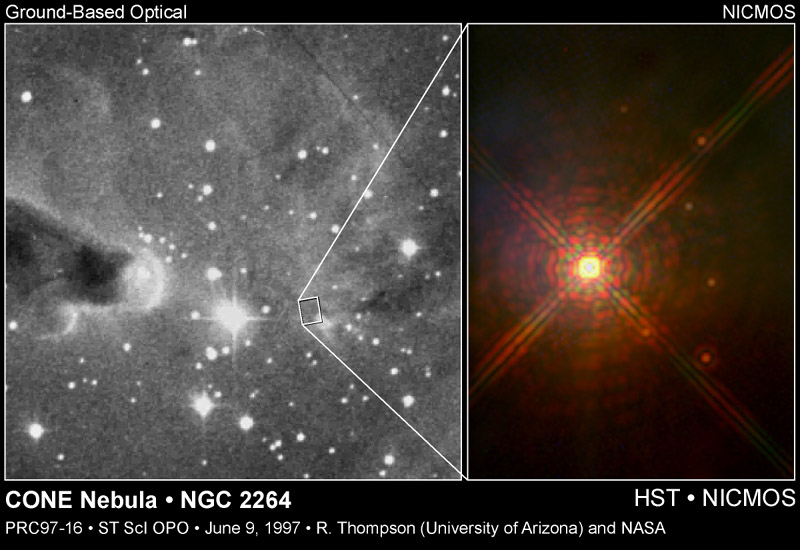
Young Suns
Credit
R. Thompson, M. Rieke and G. Schneider
(Univ. Arizona),
NASA
The star cataloged as NGC2264 IRS is normally
hidden from the inquiring gaze of
optical telescopes.
It resides in the midst of the
obscuring gas and dust
of a nearby star forming region
popularly known as the Cone Nebula.
Imaged in penetrating infrared light by
the Hubble Space Telescope's newly operational
NICMOS instrument,
this young and massive star
was found to be surrounded by six "baby" sun-like stars -
all within less than a tenth of a light-year of their "big brother".
The diffraction spikes and rings surrounding big brother are
image artifacts.
Astronomers believe that the
high speed winds generated by the massive
star compressed nearby material causing the formation of the
smaller stars in
a text book example of triggered star formation.
The newly created suns appear to lie along an otherwise invisible boundary
where the high speed gas has collided with the wall of a denser
molecular cloud.
NGC2264 IRS also seems to be the source of the outflow which created
the striking
cone shape of the optical nebula.